The H-1B visa is essentially the visa that allows foreigners from any country in the world to work in the US and eventually have the potential to be sponsored by their for Permanent Residency (or a Green Card).
FYI other posts that may be relevant to your background information include;
(for those on or wanting to obtain an E-3 visa, many of these posts are exactly relevant to you as well)
– H1B Visa Costs
– Do I Need a Lawyer for the H-1B process
– H1B Visa Quota Predictions
– 10 Easy Steps to your H-1B Visa
– Top 100 Companies that Sponsor H-1B Visas
– Transfer to an H-1B Visa from another US Visa
– H-1B Visa Lottery System
– Extension, Renewal & Change of Employers on H-1B Visa
The funny thing is now that I look at this list I have already answered almost All the possible questions any could possible have about the H1B Visa 🙂
However I should devote at least a small post to what the visa itself is, how in simple terms you get on and all they myths surrounding the H1B.
The current quota is 65,000 for people who may be granted an H-1B visa or status. (The numerical limitation was temporarily raised to 195,000 in FY2001, FY2002 and FY2003.) In addition, excluded from the ceiling are all H-1B non-immigrants who work at (but not necessarily for) universities and non-profit research facilities. This means that contractors working at, but not directly employed by the institution may be exempt from the cap.
The difference between H-1B visa and H-1B status is that Status is granted usually as a transfer while you are within the US, where as a Visa is granted by a US Consulate or Embassy outside the country. If you are on H-1B status, if you leave the US for travel, you will have to apply for your visa at a consulate abroad. The H-1B visa allows you to travel in and out of the US.
Free Trade Agreements allow a carve out from the numerical limit of 1,400 for Chilean nationals and 5,400 for Singapore nationals. Laws also exempt up to 20,000 foreign nationals holding a master’s or higher degree from U.S. universities from the cap on H-1B visas.
Renewing a visa does not count towards the annual quotas. A change of employers only count when transferring from an employer exempt from the limits (academia or research) to one that has no exemption.
The maximum duration of the visa is three years, and is extendable to six years. An exception to maximum length of stay applies in certain circumstances:
- 1 year extensions if a labor certification application has been filed and is pending for at least 365 days
- 3 year extensions if an I-140 has been approved. (application to switch to permanent residency
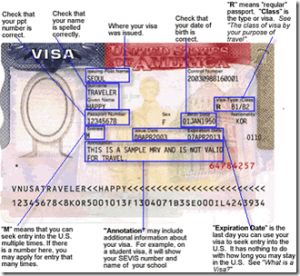
What Does The H-1B Visa Look Like?